What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Benefits & How It Works In an age where cyberattacks are increasingly sophisticated and prevalent, the security of online accounts has never been more crucial. It’s no longer enough to rely on a simple password to protect sensitive data and personal information. In fact, research shows that 81% of data breaches are caused by compromised passwords, making them a significant vulnerability in today’s digital landscape. So, how can you ensure your online security is more robust and less prone to such attacks?
The answer lies in Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)—a powerful and increasingly essential security measure that goes beyond just using a password. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide more than one piece of information to verify their identity. Instead of only entering a password, users are prompted to offer something they know (like a PIN), something they have (like a smartphone or security key), or something they are (like a fingerprint or facial recognition). This makes it much more difficult for hackers to access accounts, even if they have your password.
MFA is, how it works, and why it’s one of the most effective ways to safeguard your digital life. Whether you’re securing personal accounts or managing access for a business, understanding MFA’s benefits and implementation can dramatically improve your cybersecurity. Let’s explore how this critical security measure helps protect you from evolving cyber threats and why it should be a top priority for everyone online.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to verify their identity using two or more different factors before gaining access to an application, online account, or network. It is a critical element of a robust identity and access management (IAM) strategy. Unlike traditional systems that rely solely on a username and password, MFA adds an extra layer of security by requesting one or more additional forms of authentication, greatly reducing the chances of successful cyberattacks.
Why is MFA Crucial for Security?
The primary advantage of MFA is its ability to significantly strengthen security by ensuring users authenticate through multiple methods, not just a password. While passwords are essential, they can be vulnerable to attacks like brute force and phishing. By requiring a second form of identification, such as a fingerprint or physical hardware token, MFA makes it much more difficult for cybercriminals to compromise accounts, enhancing overall protection for your organization.
How Does MFA Function?
MFA works by requiring users to provide more than one type of verification to authenticate their identity. A common example is the use of One-Time Passwords (OTPs), which are temporary codes, often consisting of 4-8 digits. These codes are typically delivered through email, SMS, or a mobile app. OTPs are dynamically generated, either periodically or upon each authentication request, based on a predefined seed value and other factors like a counter or a timestamp. This process ensures that only authorized users can access a system or application.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an extra layer of protection used to verify a user’s identity when logging into an account or system. Instead of relying on just a password (which can be easily compromised), MFA requires two or more verification factors before granting access. These factors typically fall into three categories:
- Something you know: A password or PIN.
- Something you have: A smartphone, hardware token, or smart card.
- Something you are: Biometrics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns.
This approach reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as hackers would need to breach multiple barriers, making it far more challenging to compromise an account.
How Does MFA Work?
MFA operates through a simple but effective process:
- Enter your password: When you attempt to log in, you start by entering your regular password.
- Verification via second factor: Once the password is confirmed, the system prompts you to provide another verification factor. This could be a code sent to your mobile phone, a biometric scan, or a hardware token.
- Access granted: After successfully completing both factors, you are granted access to your account.
Types of MFA Methods
MFA methods can vary based on what factors are used for verification. Common MFA methods include:
- SMS or Email Verification: A code is sent to your phone or email that you enter to verify your identity.
- Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-sensitive codes for login.
- Biometric Authentication: Facial recognition or fingerprint scanning can be used to authenticate access.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices like USB security keys or smartcards that provide a one-time passcode.
Three Main Types of MFA Authentication Methods
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) typically relies on one of three categories of verification:
- Something you know (Knowledge): This includes passwords or PINs that only the user should be aware of.
- Something you have (Possession): This involves items like a smartphone, access badge, or a hardware token that the user physically owns.
- Something you are (Inherence): This refers to unique biometric features, such as fingerprints, voice patterns, or facial recognition, that are intrinsic to the user.
Examples of MFA Authentication Methods
MFA combines these elements to ensure secure access. Here are some examples of each:
- Knowledge:
- Passwords or PINs
- Answers to personal security questions
- One-Time Passwords (OTPs) – This can be both knowledge (you know the OTP) and possession (you need access to your phone to receive it)
- Possession:
- OTPs generated by mobile apps like Google Authenticator
- OTPs sent via text or email
- Physical access badges, USB devices, smart cards, or security keys
- Software tokens and digital certificates
- Inherence:
- Biometric authentication methods like fingerprints, facial recognition, voice recognition, or retina/iris scanning
- Behavioral biometrics, which analyze patterns like typing speed or mouse movements
Other Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
As Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) evolves, integrating machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), new methods are emerging that provide even more sophisticated ways to verify user identity. Here are some of the advanced MFA types:
Location-Based Authentication
Location-based MFA uses a user’s IP address and, when possible, their geographic location to verify identity. If the user’s location doesn’t match what’s listed on an approved list, access can be blocked. Alternatively, this data can serve as an additional verification factor along with traditional methods, such as a password or OTP, to confirm the user’s identity.
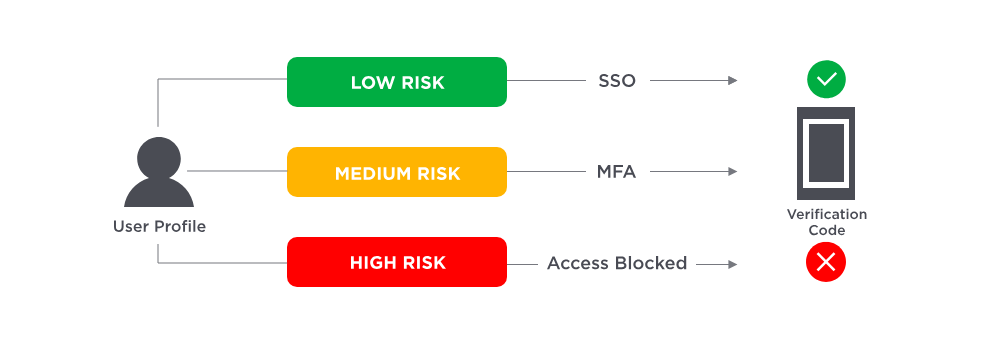
Adaptive Authentication (Risk-Based Authentication)
Adaptive Authentication, also known as Risk-Based Authentication, goes beyond standard MFA by considering additional context and user behavior to assess the risk level of each login attempt. Factors like the following are analyzed:
- Location: Where is the user trying to access the information from?
- Time: Is the user accessing data during their typical working hours or after hours?
- Device: Are they using the same device as usual, or is it a new one?
- Network: Is the connection coming from a private or public network?
Based on the answers to these questions, a risk level is assigned, which determines whether an extra authentication step is needed or if the user will be allowed to log in. For example, if a user tries to log in from an unusual location (like a cafe late at night), they may be required to enter an OTP in addition to their password. However, a user logging in from their office during normal hours may only need to provide their username and password.
Why MFA is Essential for Data Security
Cybercriminals continuously work to steal personal and organizational information. A robust, enforced MFA strategy is your first line of defense against these threats. Implementing adaptive MFA not only improves security but can also save your organization significant time and money by preventing costly data breaches in the future.
Why Should You Use Multi-Factor Authentication?
1. Enhances Account Security
The most significant benefit of MFA is enhanced security. With multiple layers of verification, even if a hacker obtains your password, they will still be unable to access your account without the second factor.
2. Reduces the Risk of Identity Theft
According to recent statistics, nearly 1 in 3 people will have their online accounts compromised in their lifetime. MFA adds a crucial layer that makes it much harder for attackers to steal your identity or access sensitive information.
3. Protects Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks trick users into revealing their passwords or other sensitive data. MFA is a strong defense against these types of attacks since even if a hacker acquires your password through phishing, they will need the second factor to successfully log in.
4. Compliance with Industry Standards
Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, require compliance with regulatory standards. Implementing MFA can help ensure your business meets the security requirements set by frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS.
5. Cost-Effective Protection
While implementing MFA may involve some setup costs, it is a highly cost-effective way to prevent data breaches and the associated financial losses, which can be significant for both individuals and businesses.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA
If you want to leverage MFA for better security, here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: MFA can’t protect you if your password is weak. Always use a strong, unique password for each account.
- Enable MFA Everywhere Possible: Many major platforms, such as Google, Facebook, and banking apps, offer MFA. Make sure to enable it on all accounts that support it.
- Choose the Right Method for Your Needs: For sensitive accounts, use more secure methods like biometrics or hardware tokens rather than SMS.
- Regularly Update and Monitor MFA Settings: Regularly review your MFA settings to ensure everything is up-to-date and functioning correctly.
Statistics on MFA and Online Security
- 80% of security breaches involve weak or stolen passwords (Source: Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report).
- Implementing multi-factor authentication can block 99.9% of automated account takeover attacks (Source: Microsoft).
- A study found that 60% of small businesses suffer from cyberattacks due to lack of proper security measures like MFA (Source: Ponemon Institute).
May you also like it:
Cold Storage: What It Is, How It Works, & Theft Protection
The Great Crypto Crash: Causes, Impact, and What’s Next
Cold Storage: What It Is, How It Works, & Theft Protection
FAQ’s
1. What does MFA stand for?
MFA stands for Multi-Factor Authentication, a security measure that requires more than one form of verification to access an account.
2. Why is MFA important?
MFA adds an extra layer of protection, making it much harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access to your accounts, even if they know your password.
3. Is MFA free to use?
Yes, many online services offer MFA for free. Some methods, like biometric authentication, may require specific devices, but SMS and authenticator apps are generally free.
4. Can I use MFA on all my accounts?
Most major platforms, including Google, Facebook, and banking apps, support MFA. It’s a good idea to enable it wherever possible.
5. How does MFA prevent phishing attacks?
MFA prevents phishing attacks by requiring an additional factor of authentication, even if the attacker obtains your password.
6. What are the best MFA methods?
The most secure MFA methods are biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition) and hardware tokens. Authenticator apps are also highly secure and widely used.
Conclusion
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a vital security tool in today’s digital world. By combining multiple layers of verification, MFA significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access and keeps your sensitive data safe from cyber threats. Whether you’re an individual seeking extra protection or a business looking to meet compliance standards, MFA is a simple yet powerful way to enhance cybersecurity.

